Cooling And Heating Curves Of A Pure Substance

Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of 30 c well below its melting point the ice is in a closed container.
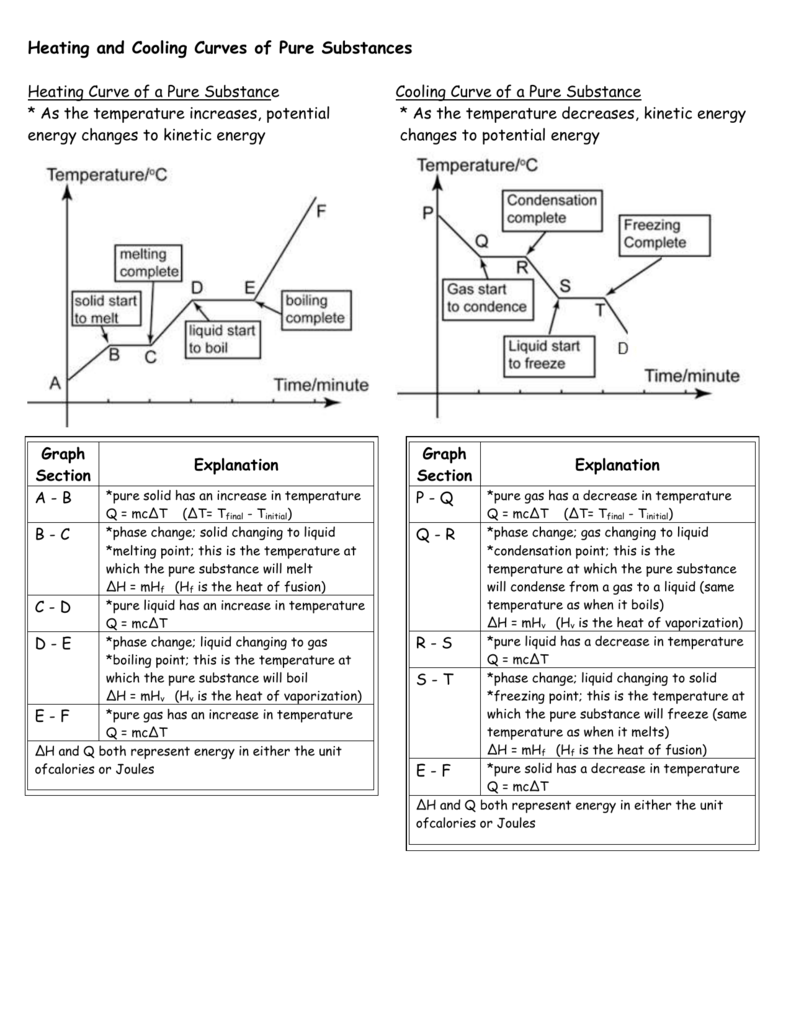
Cooling and heating curves of a pure substance. A b turns heat energy to kinetic energy. The heating cooling curve of a pure substance so basically what we did today is the heating and cooling curve of a pure substance we also needed to do a flow chart because we might have a lab next class. A solid state at any temperature below its melting point particles packed closely together can only vibrate in a fixed position a b heat energy turns to kinetic energy when heated. In this video i will explain the concept of heating and cooling curves as they applies to water and ethanol.
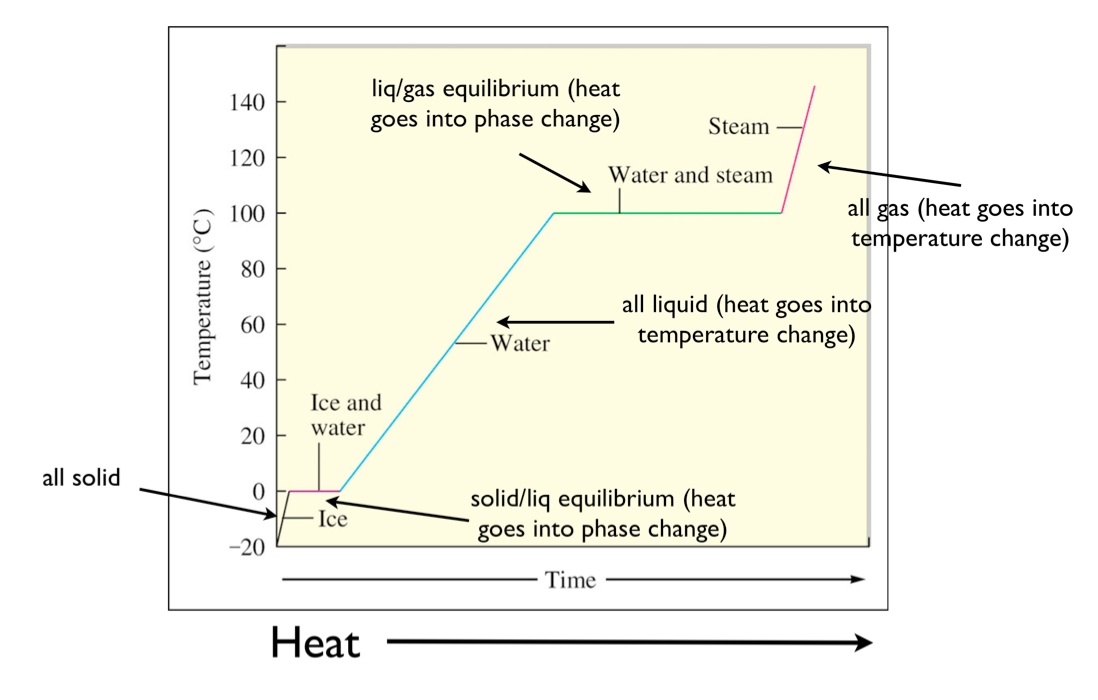
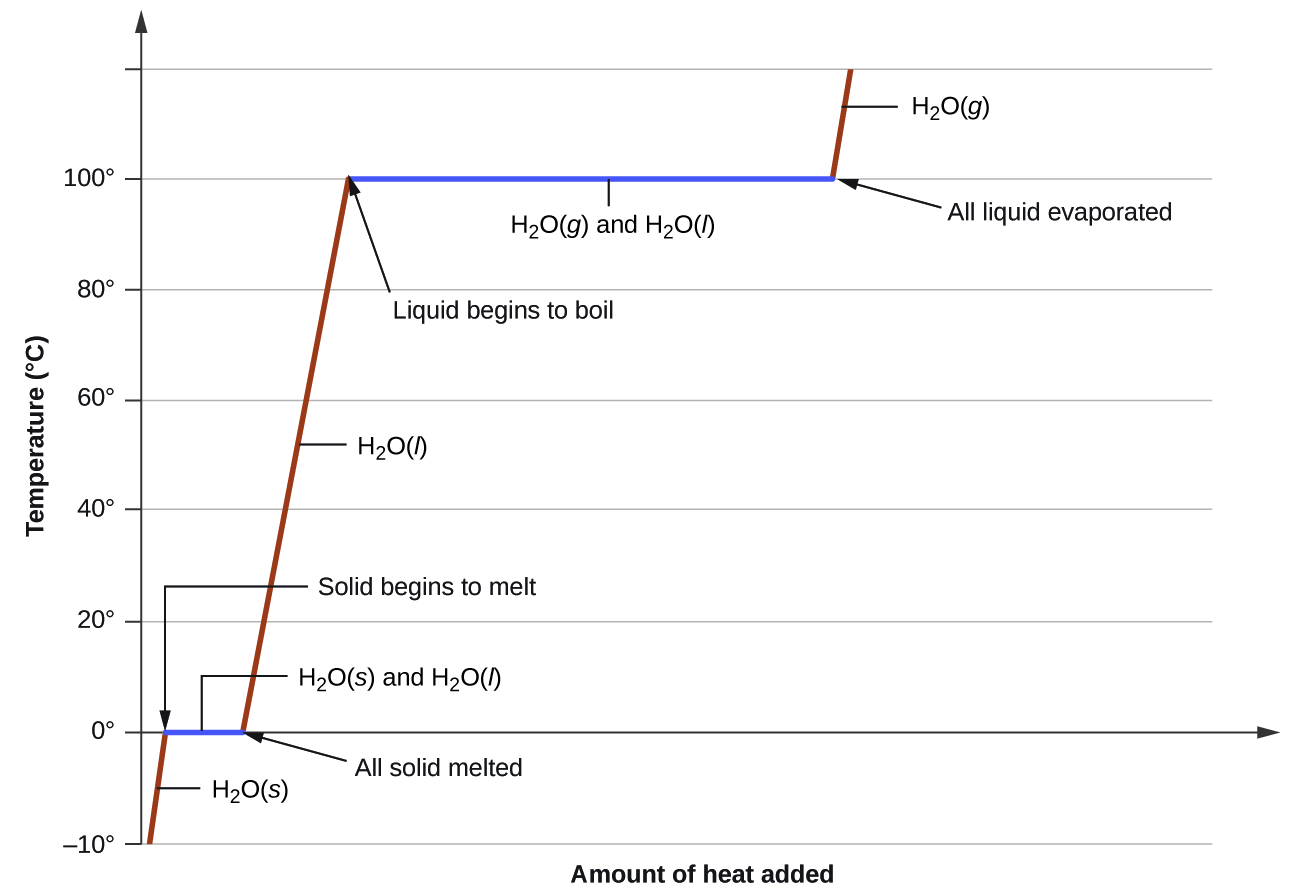
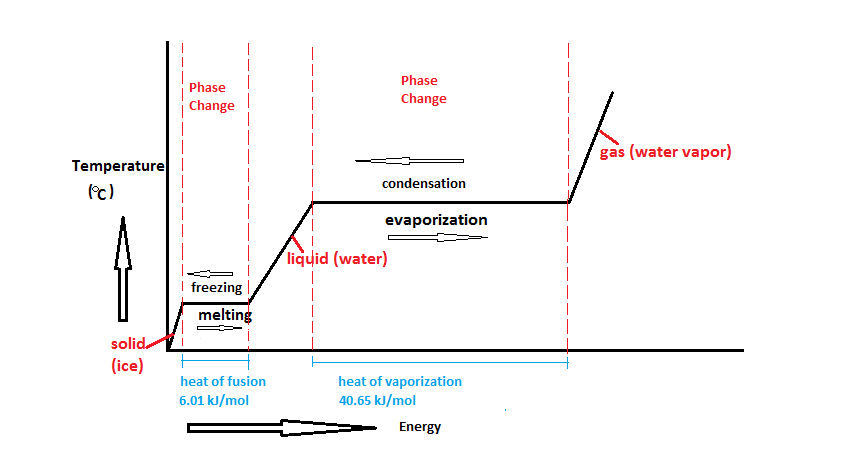
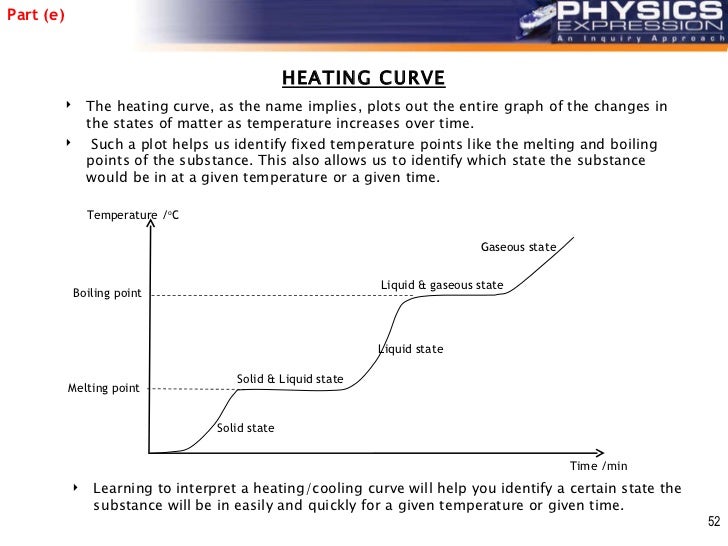
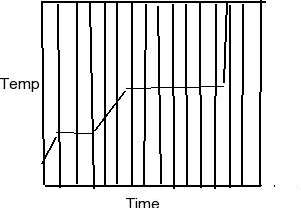
Changes of state can be investigated by measuring the temperature as a substance changes state. B is the point where it starts to melt. Figure pageindex 1 shows a typical heating curve. This class lesson was on the heating cooling curve of a pure substance.
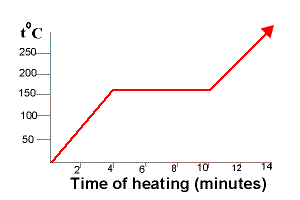
Temperature is plotted on the y axis while the x axis represents the heat that has been added. Heat a substance and measure its temperature for. The temperature stays the same when a pure substance changes state the horizontal part of the graph shows that the salol. A heating or cooling curve is a simple line graph that shows the phase changes a given substance undergoes with increasing or decreasing temperature.
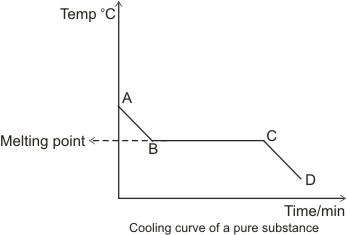
Cooling curves are the opposite. While a substance is undergoing a change in state its temperature remains constant. Each point on the graph represents a pure substance changing into a new state. They show how the temperature changes as a substance is cooled down.
Just like heating curves cooling curves have horizontal flat parts where the state changes from gas to liquid or from liquid to solid. The graph shows the cooling curve for a sample of a compound called salol. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. There are two possibilities.
As heat is steadily added to the ice block the water molecules will begin to vibrate faster and faster as they absorb kinetic energy. Plateaus in the curve regions of constant. A typical heating curve for a substance depicts changes in temperature that result as the substance absorbs increasing amounts of heat. Heating curves show how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up.
Drawing a heating curve. So a is a solid state at any temperature below melting point.