Contact Angle Surface Energy Conversion

This is commonly referred to as a contact angle measurement using the sessile drop method.
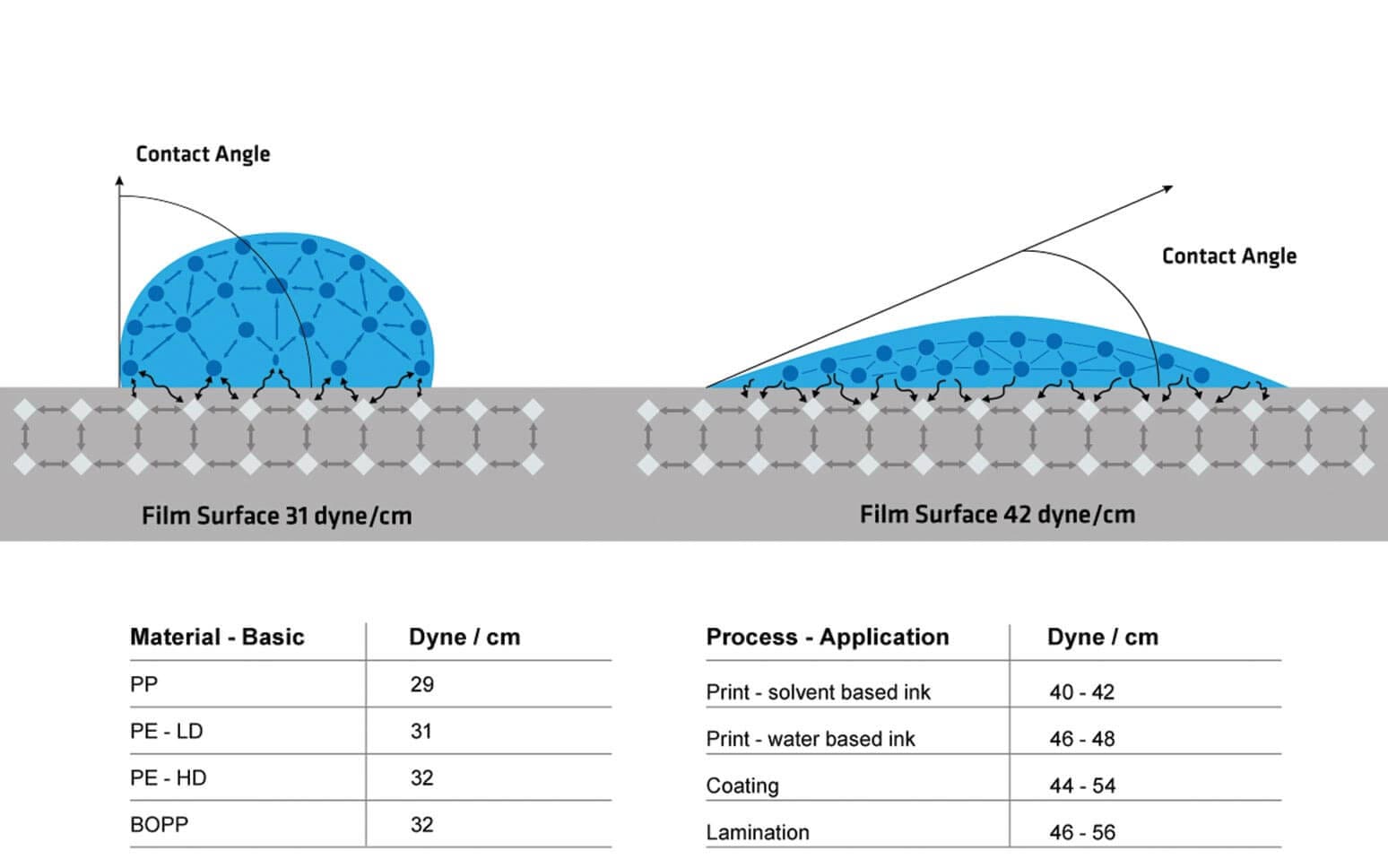
Contact angle surface energy conversion. The most common way to measure surface energy is through contact angle experiments. Static contact angle offers a quick easy and quantitative measurement of wettability. Tantec s half angle method is based on the formula for determining contact angles from the droplet dimensions. Static contact angles are also used to define the surface free energy i e.
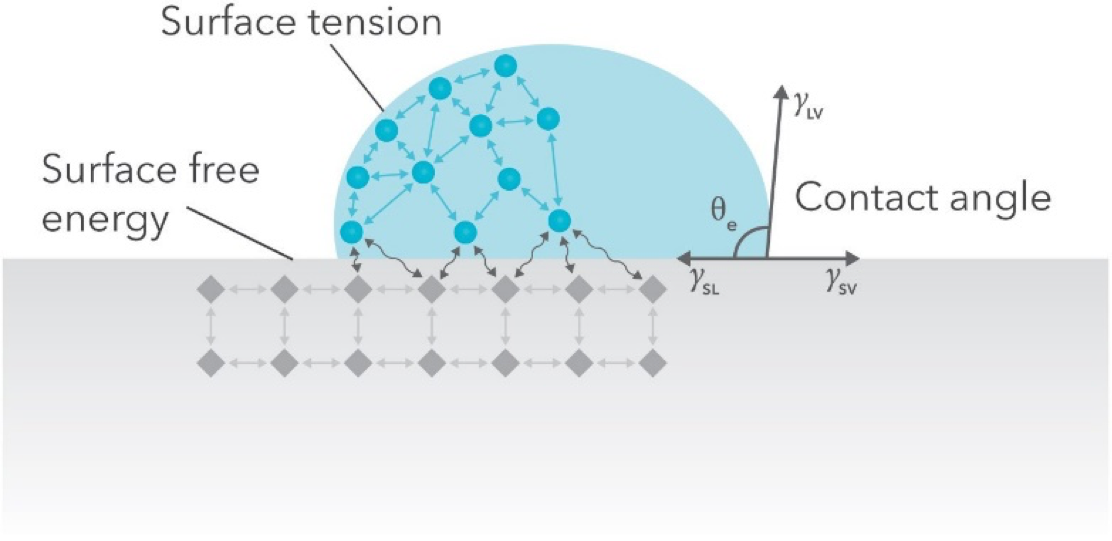
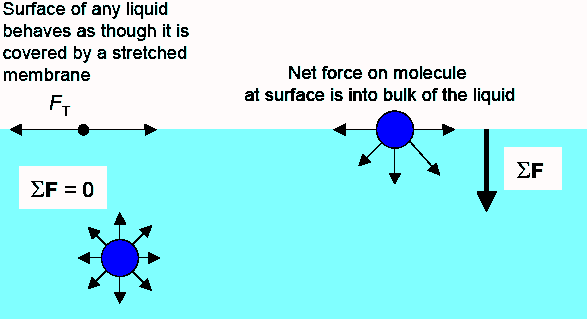
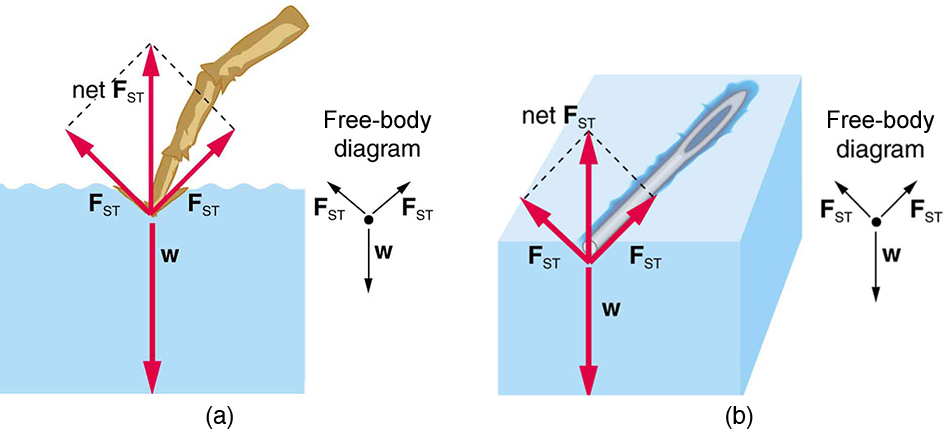
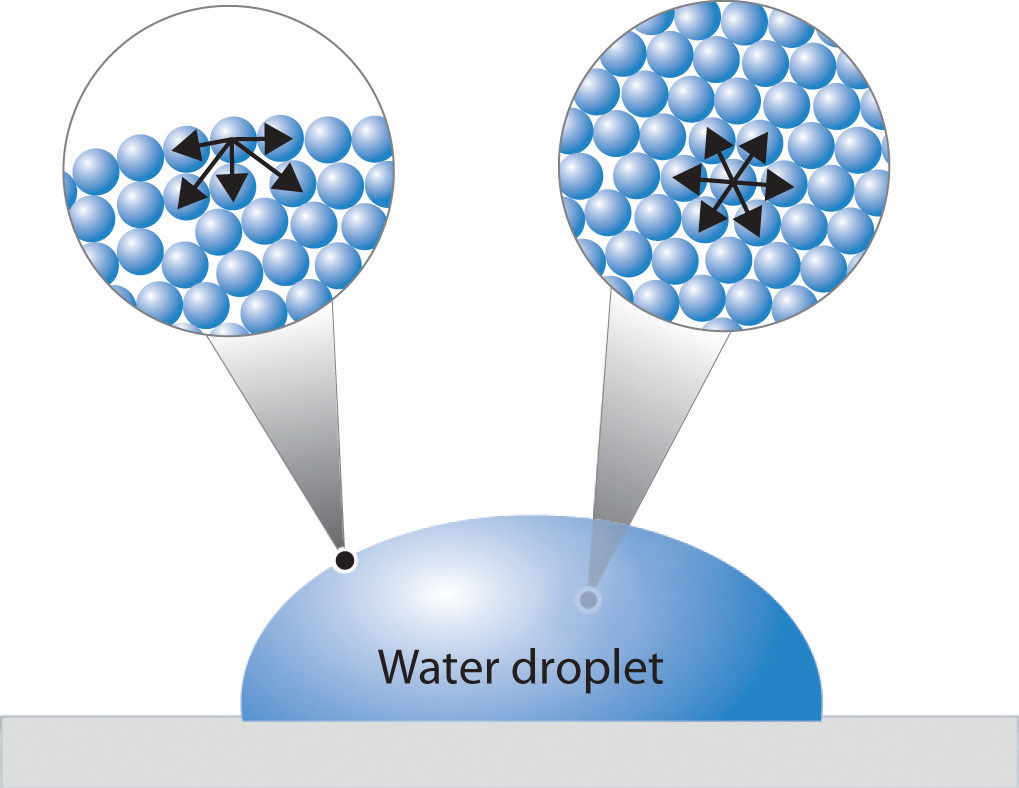
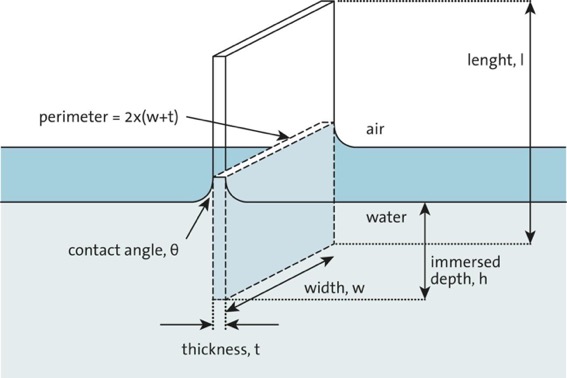
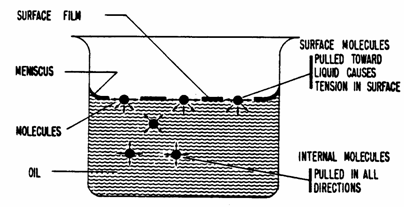
Static contact angles are by far the most measured wettability values. In this method the contact angle of the surface is measured with several liquids usually water and diiodomethane. Surface tension of solid of the substrate. The contact angle is measured as the inward angle between the base and the tangent at the point of contact between the liquid and the surface.
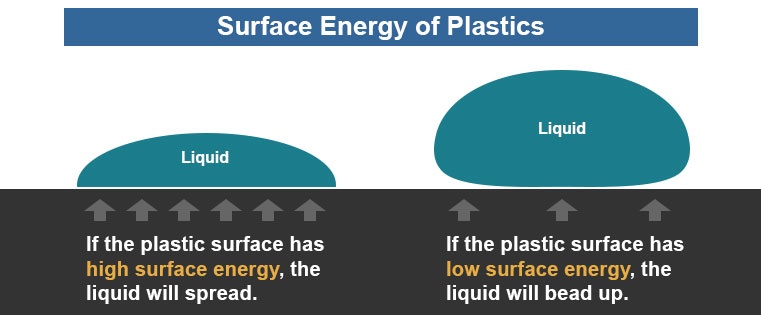
Is contact angle h is the height of a droplet and r is the radius of droplet s base see fig. Based on the contact angle results and knowing the surface tension of the liquids the surface energy can be calculated. A more general approach to understanding a surface s wettability is through surface free energy analysis. For complete data the advancing receding and static contact angles must be measured.
From the contact angle θ determined with one liquid of known surface tension only it is possible to obtain the values of the surface tensions γ sv and γ sl via the equation of state 1. The angle between the droplet outline and the solid surface is the contact angle. It is most suitable for relatively smooth and homogenous surfaces. In practice this analysis is done automatically by a contact angle meter.
This may raise the question of how we equate surface energy density units j m 2 with surface tension units n m. This value corresponds to the surface energy level in the equilibrium. Where the subscripts s and l stand for the solid s and the liquid l whilst the subscript v stands for vapor. ϒ s ϒ sl ϒ l cos θ where the inter facial.
2 arc tan h r where. The two last mentioned quantities are. I would like to calculate the surface free energy of solid by using contact angle measurement of liquid by the relation of young s equation. Once the contact angle is measured the interfacial energies can be calculated from the young laplace equation as described in eq.
By measuring the contact angle formed by probe liquids with known surface tensions values the surface free energy components are calculated using analysis models.